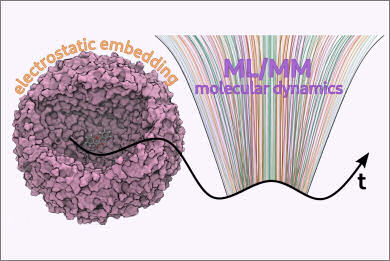
The application of quantum mechanics (QM)/molecular mechanics (MM) models for studying dynamics in complex systems is nowadays well established. However, their significant limitation is the high computational cost, which restricts their use for larger systems and long-timescale processes. We propose a machine-learning (ML) based approach to study the dynamics of solvated molecules on the ground- and excited-state potential energy surfaces. Our ML model is trained on QM/MM calculations and is designed to predict energies and forces within an electrostatic embedding framework. We built a socket-based interface of our machinery with AMBER to run ML/MM molecular dynamics simulations. As an application, we investigated the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer of 3-hydroxyflavone in two different solvents: methanol and methylcyclohexane. Our ML/MM simulations accurately distinguished between the two solvents, effectively reproducing the solvent effects on proton transfer dynamics.
Mazzeo, P.; Cignoni, E.; Arcidiacono, A.; Cupellini, L. & Mennucci, B.
Electrostatic embedding machine learning for ground and excited state molecular dynamics of solvated molecules, RSC Digit. Discov. (2024) https://doi.org/10.1039/D4DD00295D