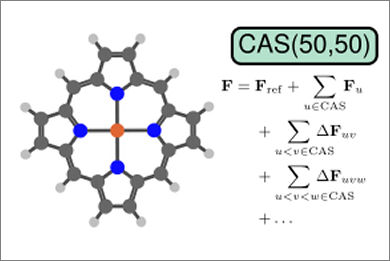
We present a novel implementation of the complete active space self-consistent field (CASSCF) method that makes use of the many-body expanded full configuration interaction (MBE-FCI) method to incrementally approximate electronic structures within large active spaces. On the basis of a hybrid first-order algorithm employing both Super-CI and quasi-Newton strategies for the optimization of molecular orbitals, we demonstrate both computational efficacy and high accuracy of the resulting MBE-CASSCF method. We assess the performance of our implementation on a set of established numerical tests before applying MBE-CASSCF in the investigation of the triplet-quintet spin gap of iron(II) porphyrin with active spaces as large as 50 electrons in 50 orbitals.
Greiner, J.; Gianni, I.; Nottoli, T.; Lipparini, F.; Eriksen, J.J. & Gauss, J.
J. Chem. Theory Comput. (2024) https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jctc.4c00388