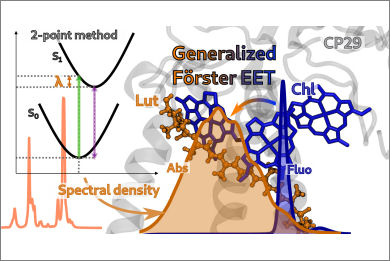
Light-harvesting complexes (LHCs) play a critical role in modulating energy flux within photosynthetic organisms in response to fluctuating light. Under high light conditions, they activate quenching mechanisms to mitigate photodamage. Despite their importance, the molecular mechanisms underlying these photoprotective processes remain incomplete. Herein, we present a computational protocol to model the energy pathways in the LHC, focusing specifically on the minor CP29 antenna complex of plants. We explore the factors that modulate the switch between the light-harvesting and quenched states. The protocol includes modeling the exciton Hamiltonian of the chlorophylls/lutein aggregate and calculating population dynamics using a kinetic model based on the Redfield-Fӧrster approach. Our analysis reveals a highly tunable excited-state lifetime for the complex, that can switch between quenched and unquenched state depending on the excitation energy of the lutein, which acts as a final quencher, in accordance with recent experiments. Moreover, we observe that the s-trans lutein conformers are more likely to exhibit characteristics of the quencher.
John, C.; Pedraza-González, L.; Betti, E.; Cupellini, L. & Mennucci, B.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2024 - https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.4c06617